Maximum Binary Tree II
We are given the root node of a maximum tree: a tree where every node has a value greater than any other value in its subtree.
Just as in the previous problem, the given tree was constructed from an list A (root = Construct(A)) recursively with the following Construct(A) routine:
If
Ais empty, returnnull.Otherwise, let
A[i]be the largest element ofA. Create arootnode with valueA[i].The left child of
rootwill beConstruct([A[0], A[1], ..., A[i-1]])The right child of
rootwill beConstruct([A[i+1], A[i+2], ..., A[A.length - 1]])Return
root.
Note that we were not given A directly, only a root node root = Construct(A).
Suppose B is a copy of A with the value val appended to it. It is guaranteed that B has unique values.
Return Construct(B).
Example 1:
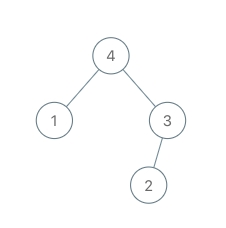

Input: root = [4,1,3,null,null,2], val = 5
Output: [5,4,null,1,3,null,null,2]
Explanation: A = [1,4,2,3], B = [1,4,2,3,5]Example 2:


Input: root = [5,2,4,null,1], val = 3
Output: [5,2,4,null,1,null,3]
Explanation: A = [2,1,5,4], B = [2,1,5,4,3]Example 3:
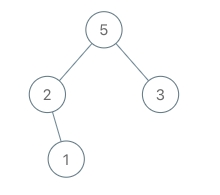

Input: root = [5,2,3,null,1], val = 4
Output: [5,2,4,null,1,3]
Explanation: A = [2,1,5,3], B = [2,1,5,3,4]Constraints:
1 <= B.length <= 100
class Solution {
public TreeNode insertIntoMaxTree(TreeNode root, int val) {
// Value is appended to the end of the array from which 'A' was constructed
// Refer "Maximum Binary Tree" for understanding completely
if (root == null) {
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(val);
return node;
}
if (root.val < val) {
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(val);
node.left = root;
return node;
}
root.right = insertIntoMaxTree(root.right, val);
return root;
}
}Last updated