Sort Items by Groups Respecting Dependencies
There are n items each belonging to zero or one of m groups where group[i] is the group that the i-th item belongs to and it's equal to -1 if the i-th item belongs to no group. The items and the groups are zero indexed. A group can have no item belonging to it.
Return a sorted list of the items such that:
The items that belong to the same group are next to each other in the sorted list.
There are some relations between these items where
beforeItems[i]is a list containing all the items that should come before thei-th item in the sorted array (to the left of thei-th item).
Return any solution if there is more than one solution and return an empty list if there is no solution.
Example 1:
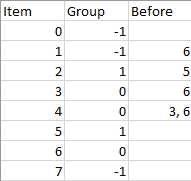
Input: n = 8, m = 2, group = [-1,-1,1,0,0,1,0,-1], beforeItems = [[],[6],[5],[6],[3,6],[],[],[]]
Output: [6,3,4,1,5,2,0,7]Example 2:
Input: n = 8, m = 2, group = [-1,-1,1,0,0,1,0,-1], beforeItems = [[],[6],[5],[6],[3],[],[4],[]]
Output: []
Explanation: This is the same as example 1 except that 4 needs to be before 6 in the sorted list.Constraints:
1 <= m <= n <= 3*10^4group.length == beforeItems.length == n-1 <= group[i] <= m-10 <= beforeItems[i].length <= n-10 <= beforeItems[i][j] <= n-1i != beforeItems[i][j]beforeItems[i]does not contain duplicates elements.
class Solution {
public int[] sortItems(int n, int m, int[] group, List<List<Integer>> beforeItems) {
// Graph creation with 2 dummy nodes (start & end) for each group
// We are creating graph like this becuase we want the nodes in 1 group to be
// together in answer
List<Integer>[] graph = new ArrayList[n + 2 * m];
for (int i = 0; i < n + 2 * m; i++)
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
int[] indegree = new int[n + 2 * m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (group[i] != -1) {
// Dummy start node to group node
graph[n + 2 * group[i]].add(i);
indegree[i]++;
// group node to dummy end node for that group
graph[i].add(n + 2 * group[i] + 1);
indegree[n + 2 * group[i] + 1]++;
}
// If 2 different group are involed always make connections with
// dummy start and end nodes
for (int x : beforeItems.get(i)) {
// If "before" is not part of a group
if (group[x] == -1) {
if (group[i] == -1) {
graph[x].add(i);
indegree[i]++;
} else {
graph[x].add(n + 2 * group[i]);
indegree[n + 2 * group[i]]++;
}
}
// If "before" is a part of group
else {
if (group[i] == -1) {
graph[n + 2 * group[x] + 1].add(i);
indegree[i]++;
} else {
if (group[i] == group[x]) {
graph[x].add(i);
indegree[i]++;
} else {
graph[n + 2 * group[x] + 1].add(n + 2 * group[i]);
indegree[n + 2 * group[i]]++;
}
}
}
}
}
// Topological Sorting
Deque<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n + 2 * m; i++)
if (indegree[i] == 0)
q.addLast(i);
int[] ans = new int[n];
int index = 0;
while (q.size() != 0) {
int node = q.pollFirst();
for (int x : graph[node]) {
indegree[x]--;
// Adding in front of queue, because we want nodes together from same group
if (indegree[x] == 0)
q.addFirst(x);
}
if (node < n)
ans[index++] = node;
}
return index == n ? ans : new int[0];
}
}Last updated