Longest ZigZag Path in a Binary Tree
Given a binary tree root, a ZigZag path for a binary tree is defined as follow:
Choose any node in the binary tree and a direction (right or left).
If the current direction is right then move to the right child of the current node otherwise move to the left child.
Change the direction from right to left or right to left.
Repeat the second and third step until you can't move in the tree.
Zigzag length is defined as the number of nodes visited - 1. (A single node has a length of 0).
Return the longest ZigZag path contained in that tree.
Example 1:
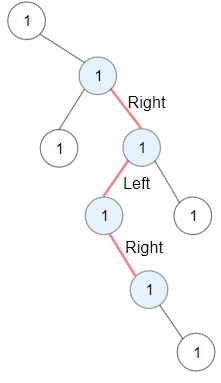
Input: root = [1,null,1,1,1,null,null,1,1,null,1,null,null,null,1,null,1]
Output: 3
Explanation: Longest ZigZag path in blue nodes (right -> left -> right).Example 2:
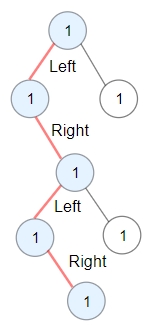
Input: root = [1,1,1,null,1,null,null,1,1,null,1]
Output: 4
Explanation: Longest ZigZag path in blue nodes (left -> right -> left -> right).Example 3:
Input: root = [1]
Output: 0Constraints:
Each tree has at most
50000nodes..Each node's value is between
[1, 100].
class Solution {
static int max = 0;
public static int longestZigZag(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return -1;// if null return -1
max = 0;
helper(root.right, 1, true);// go right
helper(root.left, 1, false);// go left
return max;
}
private static void helper(TreeNode root, int step, boolean isRight) {
if (root == null)
return;
max = Math.max(max, step);
if (isRight) {// if coming from right go left
helper(root.left, step + 1, false);
helper(root.right, 1, true);// try again from start
} else {// else coming from left then go right
helper(root.right, step + 1, true);
helper(root.left, 1, false);
}
}
}Last updated