Binary Search Tree Iterator
Implement an iterator over a binary search tree (BST). Your iterator will be initialized with the root node of a BST.
Calling next() will return the next smallest number in the BST.
Example:
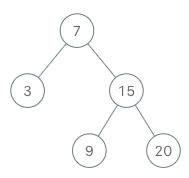
BSTIterator iterator = new BSTIterator(root);
iterator.next(); // return 3
iterator.next(); // return 7
iterator.hasNext(); // return true
iterator.next(); // return 9
iterator.hasNext(); // return true
iterator.next(); // return 15
iterator.hasNext(); // return true
iterator.next(); // return 20
iterator.hasNext(); // return falseNote:
next()andhasNext()should run in average O(1) time and uses O(h) memory, where h is the height of the tree.You may assume that
next()call will always be valid, that is, there will be at least a next smallest number in the BST whennext()is called.
class BSTIterator {
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
public BSTIterator(TreeNode root) {
adder(root);
}
public int next() {
TreeNode next = stack.pop();
adder(next.right); // This will work because in the end the AVERAGE time complexity will be O(1).
return next.val;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return stack.size() == 0 ? false : true;
}
private void adder(TreeNode temp) {
while (temp != null) {
stack.push(temp);
temp = temp.left;
}
}
}Last updated