Boundary Traversal of binary tree
Write a function to print Boundary Traversal of a binary tree. Boundary Traversal of a binary tree here means that you have to print boundary nodes of the binary tree Anti-Clockwise starting from the root. Note: Boundary node means nodes present at the boundary of left subtree and nodes present at the right subtree also including leaf nodes. For the below tree, the function should print 20 8 4 10 14 25 22 .
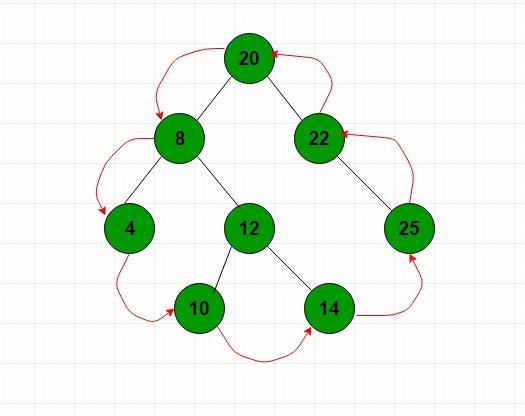
Input : The first line of input contains the number of test cases T. For each test case, there will be only a single line of input which is a string representing the tree as described below:
The values in the string are in the order of level order traversal of the tree where, numbers denote node values, and a character “N” denotes NULL child.
For example: For the above tree, the string will be: 1 2 3 N N 4 6 N 5 N N 7 N

Output: The function should print the Boundary traversal of the tree.
Your Task: This is a function problem. You don't have to take input. Just complete the function printBoundary() that takes the root node as input and returns an array containing the boundary values in anti-clockwise.
Expected Time Complexity: O(N). Expected Auxiliary Space: O(Height of the Tree).
Constraints: 1 <=T<= 30 1 <= Number of nodes<= 105 1 <= Data of a node<= 105 Example: Input: 2 1 2 3 10 20 30 40 60
Output: 1 2 3 10 20 40 60 30
Explanation: Testcase 1:
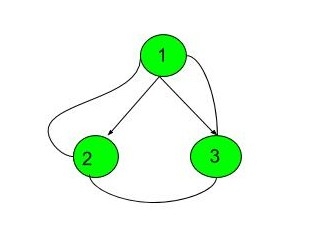
The first test case represents a tree with 3 nodes and 2 edges where the root is 1, the left child of 1 is 2 and the right child of 1 is 3. And boundary traversal of this tree prints nodes as 1 2 3.
class Solution {
ArrayList<Integer> ans;
// Left boundary is NOT same as left view
public void leftBoundary(Node node) {
// Not inserting leaf nodes here
if (node.left == null && node.right == null)
return;
ans.add(node.data);
if (node.left != null)
leftBoundary(node.left);
else
leftBoundary(node.right);
}
public void leafs(Node node) {
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
ans.add(node.data);
return;
}
// Inserting leafs from left to right
if (node.left != null)
leafs(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
leafs(node.right);
}
// Right boundary is NOT same as right view
public void rightBoundary(Node node) {
// Not inserting leaf nodes here
if (node.left == null && node.right == null)
return;
if (node.right != null)
rightBoundary(node.right);
else
rightBoundary(node.left);
ans.add(node.data);
}
public ArrayList<Integer> printBoundary(Node node) {
ans = new ArrayList<>();
ans.add(node.data);
if (node.left != null)
leftBoundary(node.left);
leafs(node);
if (node.right != null)
rightBoundary(node.right);
return ans;
}
}Last updated